In the world of Kubernetes, managing sensitive data like passwords securely is crucial. A common method involves using Base64 encoding to create Kubernetes secrets. This technique is simple yet essential for protecting passwords. Here’s how I learned about Base64 encoding and decoding to enhance security in Kubernetes secret yaml files.
Base64 Encoding: The Command
To encode a password for Kubernetes, I used:

The -n flag with echo prevents the addition of a newline character, ensuring the encoded string (bW9nZ291c2Vy) matches the original password without extra characters. This step is crucial for the integrity of Kubernetes secrets.
Decoding: Unveiling the Original
Decoding is straightforward:

This returns the original password, “mongouser”, demonstrating how to retrieve secrets for verification or management purposes.
The Newline Character Insight
A fascinating discovery was understanding the impact of the newline character in encoding. Without -n:

This outputs bW9uZ291c2VyCg==, where Cg== represents the newline character. Such nuances are vital in Kubernetes, where precision in secrets is non-negotiable.
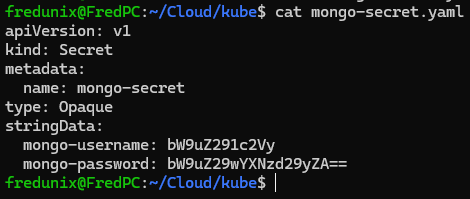
Crafting a Kubernetes Secret
Learning encoded password, to provide more secure credentials to my Kubernetes secret config files:
Conclusion
Using Base64 encoding for Kubernetes secrets is a testament to the blend of simplicity and security. Understanding the command line nuances, such as the -n flag and the importance of accurately encoding (and decoding) secrets, is key to maintaining secure and functional Kubernetes environments.
